In a world facing the challenges of climate change, resource scarcity, and a growing population, the global food industry is undergoing a significant transformation. Alternative proteins have emerged as a sustainable and innovative solution to address these pressing issues. This blog will explore the fascinating world of alternative proteins, their importance, and the exciting development in this field.
What are Alternative Proteins?
Firstly, what is protein? and why is it important?
Protein is a nutrient your body needs for the growth and repair of body tissues, being particularly important for healthy muscles and bones.
Alternative proteins refer to a diverse range of protein sources that serve as substitutes or “alternatives” to traditional animal-based proteins like meat and dairy. These proteins are derived from various plant, insect and microbial-based, or lab-grown, animal-free sources, and they aim to provide sustainable, ethical, and environmentally friendly options for consumers.
The development and consumption of alternative proteins have gained momentum due to concerns about the environmental impact of conventional animal agriculture, animal welfare, and the increasing demand for more diverse and sustainable food choices.
The goal is to offer protein-rich foods that can mimic or replace the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of animal-derived proteins, as well as enhancing the nutritional enrichment of dishes (i.e. protein bread or protein snack bars).
Alternative Protein Manufacturing Industry
The industry has experienced significant growth and innovation in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demands for plant-based food options. The market has expanded beyond traditional vegetarians and vegan consumers, attracting a broader range of people interested in diversifying their diet.
Let’s take a look at the top line of the alternative protein market and focus on the types of application, geographical trends, and the growth of vegan product and its’ market share.
Types of Application
– Meat Alternatives
Plant-based burgers, sausages, and ground meat substitutes, amongst many others, have gained substantial popularity. Companies like Quorn and Beyond Meat have played a pivotal role in shaping this segment.
– Seafood Alternatives
With concerns about overfishing and mercury contamination, the demand for plant-based seafood alternatives has risen. Products such as plant-based shrimp, fish fillets, and crab are gaining traction.
– Dairy Alternatives
The dairy alternative market includes plant-based milk, cheese, yoghurt, and ice creams. Almond, oat, soy, and coconut-based products are popular choices.
– Egg Alternatives
Vegan egg substitutes, such as plant-based scrambles and egg replacers, are becoming increasingly popular among consumer seeking cruelty-free and cholesterol-free alternatives to eggs.
– Vegan Protein Shakes
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly turning to vegan sports protein shakes. Produced with plant-based protein sources such as pea protein, rice protein, or hemp protein, these shakes deliver a rich supply of amino acids crucial for muscle recovery and growth.

Geographical Trends
The US and Canada have been at the forefront of the alternative protein movement, with a surge in consumer interest and a high number of start-ups in this sector
European countries are witnessing a growing demand for alternative proteins, driven by environmental consciousness and a rise in flexitarian, vegetarian, and vegan lifestyles.
Countries like China and India are experiencing a shift towards plant-based diets due to concerns about health, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability.
Vegan Products and their Market Share
The market is seeing an expansion of vegan offerings, which do not only cater to vegans but also appeal to a broader audience looking for alternative protein options.
The alternative protein market has witnessed exponential growth, with market share increasing steadily over the past decade. Investments from both traditional food companies and venture capitalists are indicative of the industry’s potential.
Advancements in food technology, including plant-based protein extraction and cellular agriculture, have also contributed to the market’s growth by improving the taste, texture, and nutritional value of alternative protein products.
Increased awareness of the environmental impact of traditional animal agriculture, coupled with educational campaigns on the health benefits of plant-based diets, has driven consumer interest as well as market expansion.
Why do we need Alternative Proteins?
Alternative proteins provide us with an additional option to traditional protein sources, and there are multiple reasons as to why alternative proteins are a great substitute…
- Health Benefits
- Dietary Choices – Consumers are becoming more health-conscious and are seeking protein sources that align with their dietary preferences.
- Environmental Conservation
- Traditional livestock farming has significant environmental consequences, including deforestation, water pollution, and contributing 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Alternative proteins offer a more sustainable approach to food production.
- Food Availability and Security
- Growing Populations – As the global population continues to increase, there is a growing need for protein sources that can be produced more efficiently and sustainably to meet the demand for food.
- Land and Resource Efficiency – Alternative proteins often require less land, water, and resources compared to traditional animal agriculture, making them a more efficient solution for feeding a growing population.
- Economic Considerations
- In some cases, alternative proteins can be more cost-effective to produce, especially as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved. This can lead to more affordable and accessible protein sources for consumers.
- Supply Chain Resilience
- Alternative proteins offer a way to reduce dependence on traditional agriculture, as they are less vulnerable to climate change, disease outbreaks, and other disruptions.
- Ethical and Animal Welfare Concerns
- Many consumers are increasingly concerned about animal welfare and are seeking protein sources that do not involve harm to animals. Plant-based and cultured proteins provide cruelty-free alternatives.
- Changing Consumer Preferences
- Consumer preferences are evolving, with more people embracing vegetarian, vegan, or flexitarian diets. The alternative protein sector caters to this changing landscape by providing a wider range of plant-based and lab-grown options.
We would like to add that a healthy balanced diet can be from multiple sources so you shouldn’t feel bad about eating meat and seafood and they possess their benefits too! Sourcing meat and seafood locally can also help to tackle some of the previously mentioned issues whilst supporting farmers and your local economy.
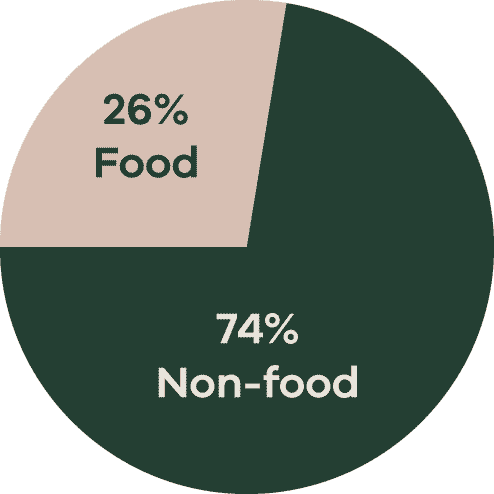
13.7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide come food and agriculture annually, equating to 26% of global greenhouse gas emission
Types of Alternative Proteins
Plant-Based Proteins
The market for plant-based protein sources has experienced substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations. The demand for plant-based protein products has surged, leading to a variety of innovative offerings and a shift toward plant-centric diets.
Plant-based proteins, such as soy, pea or fava bean come in many forms, such as powder (like isolates and concentrates), extrusions (such as protein crisps that you would have in a protein bar to improve mouth feel), or texturised protein which is then engineered by recipe developers to create met or fish analogues.
-Isolates vs. Concentrates
Not all alternative proteins are the same. They can be sourced differently, and even used differently. They are split into two groups, Isolates and Concentrates, both of which are types of protein powders
Isolates are an extracted, highly refined, form of protein, with high protein content. They are typically easier to digest due to the gluten and lactose being removed as the protein is refined, so they are useful for those suffering with digestive problems.
Concentrates are less refined than isolates. This is due to much less processing taking place. This lack of refinement results in a lower protein content, however, they retain their natural fibres and nutrients that their sources contain, that would otherwise be lost in the refinement process. Minimal processing also results in concentrates being te cheaper option of the two.
–Popular Plant-Based Protein Products
- Quorn
- Meatless Nuggets – Made from mycoprotein, a fungus-derived protein source. These nuggets are high in protein, low in saturated fat, and provide a meaty texture.
- Beyond Meat Products
- Beyond Burger – A plant-based burger made from pea protein. It provides protein, iron, and essential amino acids, with a texture and taste designed to mimic that of a traditional beef burger.
- Beyond Sausage – Plant-based sausages made from pea protein, offering a protein-rich and cholesterol-free alternative to traditional pork sausages.
- Impossible Foods
- Impossible Burger – Features a plant-based heme protein derived from soy, delivering a meaty flavour and texture. It provides protein, iron, and other essential nutrients.
- Plant-Based Protein Powder
- Pea Protein, Hemp Protein, and Rice Protein – These protein powders offer versatile options for shakes and smoothies, providing essential amino acids and supporting muscle growth.
–What’s Influenced the Increase in Consumer Demand
A variety of factors have influenced a surge in consumer demand for alternative proteins. This multifaceted evolution reflects dynamic interplay between individual choices, sustainability awareness, and innovations within the food industry.
- Environmental Concerns
- The awareness of the environmental impact of traditional animal agriculture is driving consumers to choose plant-based options to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to sustainability.
- Ethical Considerations
- Concerns about animal welfare and a desire to avoid the ethical implications of animal farming contribute to the rise of plant-based diets.
- Influence of Social Media and Celebrity Endorsements
- Social media platforms and influential figures play a significant role in promoting and influencing plant-based lifestyles. Their endorsements contribute to the mainstream acceptance of plant-based diets.
- Product Innovation and Taste Improvement
- Ongoing research and development efforts have led to the creation of plant-based products that closely mimic the taste and texture of traditional animal products, making them more appealing to a wider audience.
- Cultural Diversity
- An increase in cultural diversity, specifically in western countries, has resulted in exposure to diverse diets. This exposure will have potentially altered dietary preferences due to the acceptance of foreign culture within their own. For example, Indian cuisine is often vegetarian and a country with a large Indian population, such as the UK, will be aware of these alternative options, potentially including them within their own diets, ultimately increasing the demand for vegetarian food options.
- Trade Shows
- Trade shows such as the Plant Based World Expo are hosted across the world to showcase current, and the latest offerings and innovations, in the plant-based food industry, to customers.
Cell-Based Proteins (Lab-Grown Meat)
Cell-based proteins refer to proteins that are produced through cellular agriculture, a technology that involves growing animal cells in a controlled environment outside the animal’s body. This process enables the creation of meat, poultry, and seafood without the need of traditional animal farming. The cells are cultivated in bioreactors and provided with a nutrient-rich medium that allows them to multiply and form muscle tissues, replicating the texture and composition of conventional meat.
–Sustainability Advantages of Cell-Based Proteins
- Reduced environmental impact
- Animal welfare
- Potential to alleviate food insecurity
–Recent Advancements in Cellular Agriculture
Cellular agriculture breakthroughs are transforming food production, cultivating meat and dairy directly from animal cells. These innovations offer sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional agriculture.
- Scaling Production
- Recent advancements have focused on scaling up the production of lab-grown meat. Companies are investing in research and infrastructure to make the technology more commercially viable.
- Diversity of Products
- Innovations in cellular agriculture extend beyond beef to include poultry, seafood, and other types of meat. Companies are developing a wide range of lab-grown products to cater to diverse consumer preferences.
- Improving Taste and Texture
- Researchers and companies are continuously working to improve the taste and texture of lab-grown meat to make it more appealing to consumers. This involves refining the cellular cultivation process and optimising the nutrient medium.
- Reducing Costs
- One of the challenges for lab-grown meat has been the cost of production. Recent advancements aim to reduce production costs through process optimisation, innovations in nutrient formulations, and economies of scale.
- Regulatory Approvals
- Some lab-grown meat products have received regulatory approvals in various regions, marking a significant milestone in the industry’s development. This progress paves the way for greater acceptance and market entry.
The continued progress in this field has the potential to revolutionise the way we produce and consume meat, addressing environmental, ethical, and resource sustainability challenges associated with conventional meat production.
Insect Protein
Insect proteins are gaining attention as an unconventional yet eco-friendly protein source that has the potential to address global food sustainability challenges. Edible insects have been consumed in various cultures for centuries, today, they are being explored as a viable and environmentally friendly protein alternative to traditional livestock.
–Cultural Acceptance and Nutritional Value
Insects are a traditional part of diets for many cultures, providing them with essential nutrients and proteins. However, cultural acceptance of insect consumption varies globally. While some societies have a long history of insect consumption, others are much less familiar with the practice.
With regards to their nutritional value, insects are rich in high-quality proteins, essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. They also contain healthy fats, such as Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. Additionally, insects are a sustainable source of nutrition, requiring less land, water, and feed compared to traditional livestock.

–Start-Ups and Initiatives in Insect-Based Protein Products
- Entomo Farms
- Entomo Farms, based in Canada, is one of the largest cricket farms globally. They produce cricket protein powder, and whole roasted crickets, amongst other insect-based products. Their focus is on promoting the nutritional and environmental benefits of insect consumption.
- Ynsect
- Ynsect, headquartered in France, specialises in farming mealworms and turning them into protein-rich ingredients. They focus on providing sustainable and high-quality insect products for use in animal feed, plant fertilisers, and food products.
- Bugsolutely
- Operating in Thailand, Bugsolutely produces cricket-based pasta, aptly named “Cricket Pasta”. This innovative product combines the nutritional benefits of crickets with the familiarity of pasta, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
- Chapul
- Based in the US, Chapul focuses on producing cricket protein bars. Their products are designed to appeal to health-conscious consumers, as well as those looking for sustainable protein sources. The bars come in various flavours, combining taste and nutrition.
Microbial Proteins
Microbial-based proteins refer to proteins that are produced using microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, or fungi. This approach involves harnessing the natural ability of these microorganisms to synthesise proteins through fermentation or other biotechnical processes. Microbial-based proteins offer a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional protein sources.
The primary types of microbial-based proteins include:
- Single-Cell Proteins (SCP)
- Single-cell proteins are produced by cultivating microorganisms on a substrate rich in nutrients. The process often involves bacteria, yeast, or fungi, which consume the nutrients and produce protein-rich biomass. The resulting product can be harvested and used as a protein source.
- Yeast Proteins
- Yeast, particularly species like Saccharomyces Cerevisiae, can be modified or engineered to express specific proteins, and the resulting biomass can be processed into protein-rich products.
- Fungal Proteins
- Fungi can be used to produce proteins through fermentation. Fungal proteins may have diverse applications, including food and feed.
- Bacterial Proteins
- Certain bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E.coli), can be engineered to produce specific proteins. Bacterial fermentation processes are often used in biotechnology to generate proteins for various application, including pharmaceuticals and industrial processes.
–Applications of Microbial Proteins
- Food and Beverages – Microbial-based proteins can be used as ingredients in various food products, including protein-rich snacks, and fermented foods.
- Animal Feed – Single-cell proteins and microbial biomass can serve as valuable components in animal feed formulations, providing a sustainable protein source for livestock and aquaculture.
- Pharmaceuticals – Microbial-based proteins play a crucial role in the production of therapeutic proteins, vaccines, and other biopharmaceuticals.
- Biotechnology and Industrial Processes – Microbial proteins are utilised in biotechnological applications, including enzymes for industrial processes, biobased materials, and biofuel production.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Common Challenges within the Alternative Protein Industry
Having recently experienced significant growth, it’s no surprise this growth has come with its challenges. The main challenges the industry is facing are:
- Scalability – Many alternative protein technologies face challenges in scaling up production to meet the growing demand. Achieving cost-effective large-scale production remains a hurdle for some companies, particularly in the cultured meat and fermentation-based protein sectors.
- Consumer Acceptance – Convincing consumers to adopt alternative protein products, especially those that are unfamiliar, can be challenging. Overcoming taste, texture, and perception barriers requires effective marketing, education, and continual product innovation.
- Cost of Production – The cost of producing alternative proteins, especially cultured meat, is currently higher than traditional animal agriculture. Innovations and advancements are needed to reduce production costs and make alternative proteins more competitive in the market.
- Regulatory Hurdles – Regulatory frameworks for alternative proteins are still evolving, and navigating approval processes can be complex and time-consuming. Companies must work with regulatory agencies to ensure the safety and labelling of their products.
- Supply Chain Integration – Integrating alternative proteins into existing food supply chains presents logistical challenges. Developing efficient distribution channels, partnerships with retailers, and collaborations with food service providers are crucial for market accessibility.
- Technological Innovation – Continuous innovation is essential for improving the taste, texture, and nutritional profiles of alternative protein products. Advancements in biotechnology, cellular agriculture, and food science are necessary to drive the industry forward.
Insights into the Future of Alternative Proteins
– Technological Advancements
Ongoing technological advancements will play a crucial role in overcoming scalability and cost challenges. Continued research in cellular agriculture, fermentation processes, and plant-based innovations is expected to lead to breakthroughs in production efficiency.
– Diversification of Product Offerings
As innovation continues, this will provide a wider variety of alternative protein products, tailoring to the tastes of different cultures and people in general.
– Global Market Expansion
As consumer awareness and acceptance grows, alternative proteins are expected to gain traction in diverse markets globally. Emerging economies may play a significant role in the adoption of alternative protein technologies.
– Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations between alternative protein companies and traditional food industry players can accelerate market access and supply chain integration. Partnerships may also lead to the development of hybrid products combining alternative proteins with traditional ingredients.
– Increased Investment
The alternative protein industry is likely to attract increased investment from venture capital, private equity, and even traditional meat producers. This influx of capitol can fuel research and development, leading to further innovations and market growth.
– Addressing Food Security
Alternative proteins can contribute to global food security by providing sustainable protein sources that require fewer resources and have a lower environmental impact. As the global population grows, the role of alternative proteins in ensuring a resilient and efficient food supply is expected to become increasingly significant.
Government policies and incentives could play a significant role in shaping the development and growth of the alternative protein industry. Some examples of how government involvement could be beneficial are:
- Research funding
- Investment incentives
- Educational Incentives
Personal Choices and Impact
The food choices we make have a profound impact on the environment and our collective future. By considering the environmental implications of our diets, we can contribute to positive change. Let’s explore how alternative proteins play a crucial role in conservation and sustainability.
Alternative Proteins and Conservation
- Alternative proteins have a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional animal agriculture. Choosing these alternatives, even from time to time, help conserve land, water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Traditional livestock farming often leads to deforestation and habitat destruction. Alternative proteins contribute to conversation by requiring less land and minimising the impact on natural habitats.
- Opting for alternative seafood products helps preserve marine ecosystems by mitigating overfishing and supporting biodiversity. It’s a step towards ensuring the health and balance of our oceans.
How to incorporate Alternative Proteins into your Diet
- Educate Yourself – Learn about alternative protein sources and their benefits. Stay informed about the environmental impact of different food choices to make conscious decisions.
- Exploring New Recipes – Embrace variety by exploring plant-based recipes. There are countless delicious and nutritious options waiting to be discovered!
- Gradual Transition – Consider making gradual changes to your diet. Start by incorporating one or two plant-based meals a week and gradually increase as you become more comfortable with the shift.
Summary
Alternative proteins represent a promising and necessary evolution in the food industry. As we seek to address the challenges of a changing world, these innovative protein sources offer a path to more sustainable, ethical, and nutritious diets. By understanding and embracing alternative proteins, we can play a vital role in shaping the future of food and ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
How can we help?
Lehmann Ingredients have a 35 year history in the sourcing and supply of food ingredients for customers both in and outside of the UK. We are trusted suppliers of high-quality alternative protein products to a number of established companies from start-ups to more established companies leading in various retail categories, such as cereals and sports nutrition.
Contact a member of our team by emailing enquiries@lehmanningredients.co.uk or calling +44 (0) 1524 581560
Request a Sample
used in articles.



